Time Management
Activity planning
Activity planning in project
management involves defining, sequencing, and estimating the
duration of tasks (activities) to achieve project goals, ensuring efficient
resource allocation and timely completion.
Types of Activities
•
Sequential
Activities: These are tasks that must be completed
in a specific order. For example, designing a product
must precede manufacturing it.
•
Parallel
Activities: These are tasks that can be executed simultaneously without dependencies. For instance, while the design team
works on product design, the marketing team can start creating promotional
materials.
•
Critical
Path Activities: These are activities that, if delayed,
would directly impact the project's overall timeline. The critical path is the longest sequence
of dependent activities that determine the shortest possible duration
for completing the project.
Scheduled development and control
Scheduled development involves creating
a project schedule, while schedule control focuses on monitoring the
schedule, identifying variances, and taking corrective actions to ensure the project stays on track and meets its deadlines.
Scheduled Development
•
Defining Tasks and Activities: The first step is to break down the project into smaller,
manageable tasks and activities.
•
Determining Dependencies: Identify which tasks depend on others and the order in which
they need to be completed.
•
Estimating Durations: Estimate the time required
for each task and activity.
•
Resource Allocation: Assign resources (people, equipment,
etc.) to each task.
•
Creating the
Schedule: Use
project management tools (e.g., Gantt charts,
PERT charts) to visually represent
the project schedule.
Schedule Control (Monitoring and Managing the Schedule)
Monitoring Progress:
Regularly track
the progress of each task and activity against the baseline schedule.
Identifying Variances:
Compare actual progress with planned progress
and identify any deviations or variances.
Analyzing Variances:
Investigate the reasons behind
the variances and determine their impact on the project
schedule.
Taking Corrective Actions:
Implement corrective actions to address
the variances and get the
project back on track.
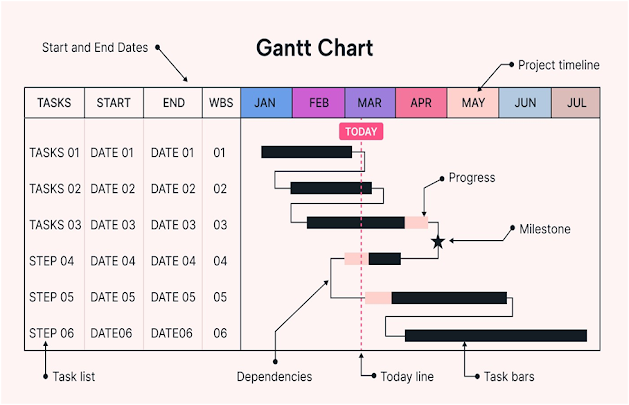
Gantt chart
What is Gantt chart?
•
A Gantt chart is a graphical representation of a project
schedule, showing tasks, their start and end dates, durations, and dependencies
•
In project management, a Gantt chart is
a visual tool, often a bar chart, used to plan, schedule, and track project
tasks, their durations, and dependencies, helping to manage timelines and progress effectively.
Key
Components
•
Tasks: The individual activities required to complete the project.
•
Timeline: The schedule,
showing when each task will take place.
•
Dependencies: Relationships between
tasks where one task's start or finish depends on another.
•
Progress: Visual representation of how much of each task has been completed.
Key
Components
•
Tasks: The individual activities required to complete the project.
•
Timeline: The schedule,
showing when each task will take place.
•
Dependencies: Relationships between
tasks where one task's start or finish depends on another.
•
Progress: Visual representation of how much of each task has been completed.





0 comments:
Post a Comment